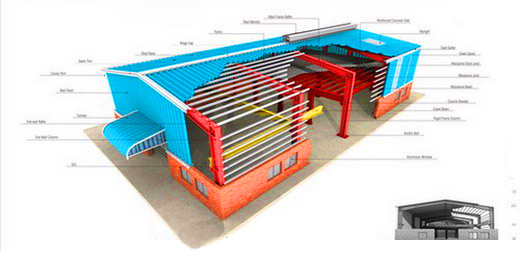
- Anchor Bolts: Bolts used to anchor structural members to a concrete floor, foundation or other masonry support. Term generally refers to bolts that secure columns and jambs to the concrete slabs.
- Base Plate: A shop-welded, pre-punched plate on that portion of a structural column that rests on the concrete foundation and is secured by anchor bolts.
- Bay (Interior): The space between frame center lines in the lengthwise direction of the building.
- Brace Rods: Rods used on roof and sidewalls of some buildings to transfer wind, seismic, and lateral crane forces to the foundation.
- Built-up Section: A structural member, usually an
I
shape, made from individual web and flange flat plates by welding them together. C
Section: A member cold formed from steel coil in the shape of aC
, used primarily in bearing frame end walls and framed openings.- Canopy: Any overhanging or projecting structure with its extreme end unsupported.
- Clear Span: The distance or clear and unobstructed opening between two supports of a beam; when used with a rigid frame, this is generally less than the nominal building width.
- Column: A primary structural member used in a vertical position to transfer loads from roof beams, trusses or rafters to the foundation.
- Corner Column: A
C
channel orI
section located at the corner of a bearing frame end wall, or a primary frame column at a main end frame. - Design Code (Design standard): The building code used in a particular area to govern building design.
- Eava Canopy: A roof extension beyond the sidewall of a building.
- Eava Fascia: Trim used to close off the top of sidewall panels in lieu of Eave gutter or eave trim.
- Eava Height:The vertical dimension from finished floor to top of eave strut.
- Eava Strut: A cold formed structural member at the eave to support roof and wall panels; also transmits forces due to wind on end wall from roof bracing to wall bracing.
- Erection: The assembling of pre-engineered components to form a complete structure.
- Erection Drawing: Drawings showing the roof framing plan, wall framing plan, end wall framing, cross section, and other parts of the building.
- Frame: Primary structural members, made up of columns and rafters, which support the secondary framing of girts and purlins.
- Gable: The triangular portion of the end wall of a building, directly under the sloping roof and above the eave line.
- Girder: A main horizontal or near horizontal structural member that supports vertical loads.
- Girt: A secondary horizontal structural member attached to sidewall or end-wall columns to which wall covering is attached and supported horizontally, usually a cold-formed
Z
shape. - Gutter: A light gauge channel member installed at the eave, valley or parapet for the purpose of carrying water from the roof to the drains or downspouts.
- Insulation: Any material used in building construction for the reduction of thermal transfer, or in some cases for reduction of fire hazard.
- Louver: An opening provided with fixed or adjustable blades to allow airflow.
- Mezzanine: A second floor above the ground floor. An intermediate level between floor and ceiling, occupying a portion of the floor space.
- Panel: Ribbed configuration metal sheets used for roof and wall covering.
- Purlin: A secondary, cold-formed horizontal structural member located in the roof to support sheeting that is itself supported by the rafters. Purlins in some buildings overlap at frames to form a continuous design.
- Rafter: A fabricated roof-framing member that supports the roof secondary framing members.
- Ridge Vent: Circular or continuous vent placed at the ridge to produce air movement through the building.
- Sag Rod or Angle: Tie rods or angles located between the webs of girts or purlins to provide lateral web stability and to limit the deflection of the girt or purlin in the direction of the weak axis. Also known as a purlin brace.
- Self-drilling Screw: A fastener that drills and taps its own hole. Used as a fastener for attaching panels to purlins and girts.
- Self-tapping Screw: A fastener that taps its own threads in a predrilled hole. Used for attaching panels to purlins and girts, for stitching panel sidelaps, and for trim and flashing.
- Skylight: A roof accessory to admit light, normally mounted on a curbed framed opening.
- Trim: Light gauge metal used in the finish of a building, especially around openings and at intersection of surfaces. Often referred to as flashing.
- Turn Key Construction service: Construction service that includes all phases of construction in a single contract.
Z
Section: A girt or purlin; a member cold-formed from steel coil in the shape of a blockZ
with stiffener lips.